Shanghai Silicate Institute and others made progress in the design of highly active hydrogen evolution catalysts
[ Instrument R & D of Instrument Network ] Designing a low-cost, highly active hydrogen evolution catalyst for efficient hydrogen production is an important part of establishing a hydrogen energy system. The two-dimensional layered chalcogenide MoS2 has the advantages of simple preparation, stable structure, and adjustable catalytic activity, so It is regarded as a very promising catalyst for hydrogen production from acidic electrolyzed water. However, most of its high active sites are limited to limited edges. How to realize the activation of MoS2 in-plane (Basal Plane) sites is the key to promoting its practical application.
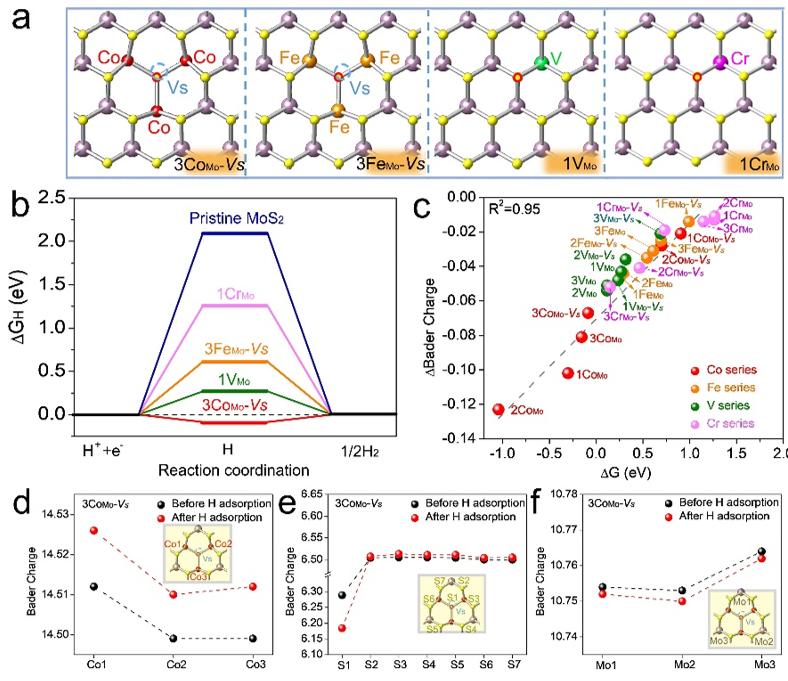
Recently, the computational electrochemistry team led by Liu Jianjun, a researcher at the Shanghai Institute of Ceramics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, and the nanomaterials research team of Fan Hongjin, a professor at Nanyang Technological University in Singapore, have made progress in designing the in-plane catalytic structure of MoS2. Theoretical calculations found that the catalytic adsorption site (S) and the transition metal connected to form a regional active center. The concept of regional electronegativity was first proposed for catalyst design, and different transition metal atoms (V, Cr, Co, Ni) were selected to dope the MoS2 surface. Different local structures are formed, and the charge transfer ability of the MoS2 basal surface is regulated by different TM-S chemical bond characteristics to optimize the catalytic activity of hydrogen evolution.
Charge transfer or charge exchange, referred to as charge transfer. Refers to the charge transfer process that occurs when positive ions collide with neutral atoms. At this time, the positive ion will capture a valence electron in the atom to become an atom; the atom will become a positive ion due to the loss of a valence electron. The charge transfer process belongs to the second type of inelastic collision process. In a collision, the potential energy of colliding particles is transferred from one side to the other.
Based on close cooperation between theoretical calculations, experimental synthesis and electrochemical characterization, it was found that the triangular cobalt-doped MoS2 basal plane with central sulfur vacancies (3CoMo-VS) exhibits excellent catalytic properties for hydrogen evolution at a current density of 10 mA cm-2 The potential is only 75 mV, and the Tafel slope is 57 mV dec-1, which is one of the materials with excellent catalytic performance for the hydrogen production of two-dimensional MoS2 electrolyzed water.
The production principle of hydrogen production from electrolyzed water:
When direct current is applied to some aqueous electrolyte solutions, the decomposed substances have nothing to do with the original electrolyte. What is decomposed is water as a solvent, and the original electrolyte remains in the water. For example, sulfuric acid, sodium hydroxide, potassium hydroxide, etc. belong to this type of electrolyte. When electrolyzing water, since pure water has a low ionization degree and low conductivity, it is a typical weak electrolyte, so the aforementioned electrolyte needs to be added to increase the conductivity of the solution, so that the water can be smoothly electrolyzed into hydrogen and oxygen
In addition, the team of Liu Jianjun systematically studied the four classic doping defects of MoS2 and the boundary structure (transition metal atoms replace Mo, S-vacancy, Mo-edge and S-edge). Different transition metal elements regulate the electronic state and the electrocatalytic activity of anions and cations . The regional electronegativity (Ψ) is proposed as a catalytic activity descriptor, which establishes the quantitative relationship between the coordination environment, the electronegativity of doped atoms, the atomic radius and the number of valence electrons and the region electronegativity, providing a theoretical basis for high activity screening .
Adapter Sleeves are the most commonly used components for locating bearings with a tapered bore onto a cylindrical seat as they can be used on:
plain shafts
stepped shafts
They are easy to install and require no additional location on the shaft:
When used on plain shafts, the bearing can be located at any position on the shaft.
When used on stepped shafts together with an L-shaped spacer ring, the bearing can be accurately positioned axially, thereby facilitating bearing mounting and dismounting.
Adapter Sleeves
Adapter Sleeves,Bearting Adapter Sleeves,Adapter Sleeves For Inch Shafts,Metric Shaft Adapter
Ningbo Ritbearing Imp & Exp Co.,Ltd. , https://www.nbbearing.de